Antwort What does ESG stand mean? Weitere Antworten – What is ESG in simple words
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ESG-final-fc9c8799d2d34234a895cbab621c21ad.png)
ESG means using Environmental, Social and Governance factors to assess the sustainability of companies and countries. These three factors are seen as best embodying the three major challenges facing corporations and wider society, now encompassing climate change, human rights and adherence to laws.Environmental, social and governance
Environmental, social and governance (ESG) is a framework used to assess an organization's business practices and performance on various sustainability and ethical issues.ESG stands for environmental, social and governance. These are called pillars in ESG frameworks and represent the 3 main topic areas that companies are expected to report in.

What is ESG short of : ESG stands for environmental, social, and governance.
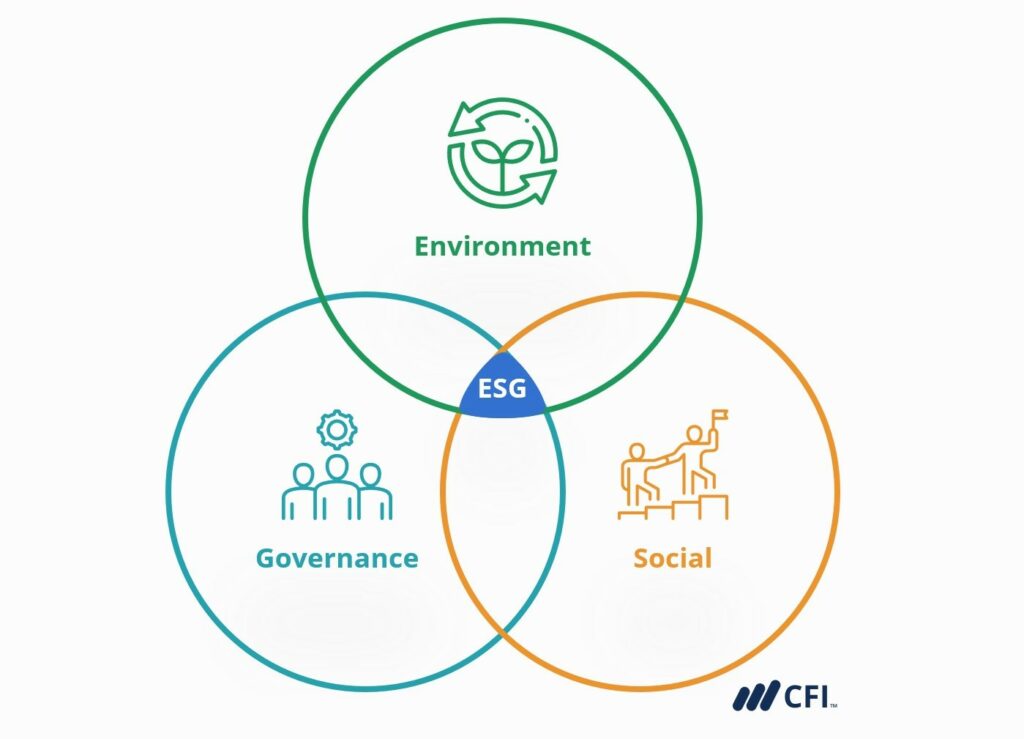
What are the 3 pillars of ESG
The three pillars of ESG are:
- Environmental – this has to do with an organisation's impact on the planet.
- Social – this has to do with the impact an organisation has on people, including staff and customers and the community.
- Governance – this has to do with how an organisation is governed. Is it governed transparently
What is the main goal of ESG : The goal of ESG is to capture all the non-financial risks and opportunities inherent to a company's day to day activities.
The importance of ESG for businesses and investors. ESG functions as a valuation technique that takes into account environmental, social and governance issues. ESG in the private sector is a set of criteria used to evaluate a company's risks and practices.
Companies with a low ESG score are thought to have the worst environmental, social, and governance impacts. Undesirable ESG scores have also been linked to rising poverty levels in the communities where the firm operates, as well as poor employee mental health.
What are the big 4 of ESG
In this context, the Big 4 accounting firms – Deloitte, PwC, Ernst & Young (EY), and KPMG – play a pivotal role in shaping corporate strategies, reporting practices, and, ultimately, the sustainability divide.Environmental and societal issues, such as climate change, biodiversity loss, modern slavery, inequalities, food security and others are interconnected and lead to risks and opportunities for both, businesses, and society.ESG stands for environmental, social and governance. These are called pillars in ESG frameworks and represent the 3 main topic areas that companies are expected to report in.

Critics portrayed ESG investing as primarily motivated by political concerns and a potential drag on returns. Additionally, some critics have raised concerns about the complexity and reliability of ESG metrics.
Why is ESG criticized : One of the biggest criticisms of ESG is that it perpetuates what it was partly designed to stop – greenwashing.
What is negative about ESG : Lack of Standardization: ESG frameworks lack uniformity, making it challenging to compare and assess companies on a consistent basis. The absence of standardized metrics and reporting practices can lead to confusion, greenwashing, and difficulty in accurately measuring ESG performance.
What are the 3 P’s of ESG
The Ps refer to People, Planet, and Profit, also often referred to as the triple bottom line. Sustainability has the role of protecting and maximising the benefit of the 3Ps. Green programs take care of people.
The three pillars of ESG are:
- Environmental – this has to do with an organisation's impact on the planet.
- Social – this has to do with the impact an organisation has on people, including staff and customers and the community.
- Governance – this has to do with how an organisation is governed. Is it governed transparently
In December 2022, Florida announced that it was taking $2 billion out of the management of BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager (and biggest lightning rod for ESG criticism). This was the largest such divestment thus far. These attacks have been coordinated.
Why are esgs controversial : Critics say ESG investments allocate money based on political agendas, such as a drive against climate change, rather than on earning the best returns for savers.



