Antwort What is an example of ESG? Weitere Antworten – What are examples of ESG

The criteria used include these examples:
- Fair pay for employees, including a living wage.
- Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) programs.
- Employee experience and engagement.
- Workplace health and safety.
- Data protection and privacy policies.
- Fair treatment of customers and suppliers.
- Customer satisfaction levels.
ESG means using Environmental, Social and Governance factors to assess the sustainability of companies and countries. These three factors are seen as best embodying the three major challenges facing corporations and wider society, now encompassing climate change, human rights and adherence to laws.ESG considerations could include reducing energy consumption (and associated costs), making your workforce and boardroom more diverse, and making customers aware of the sustainability of your goods and services.
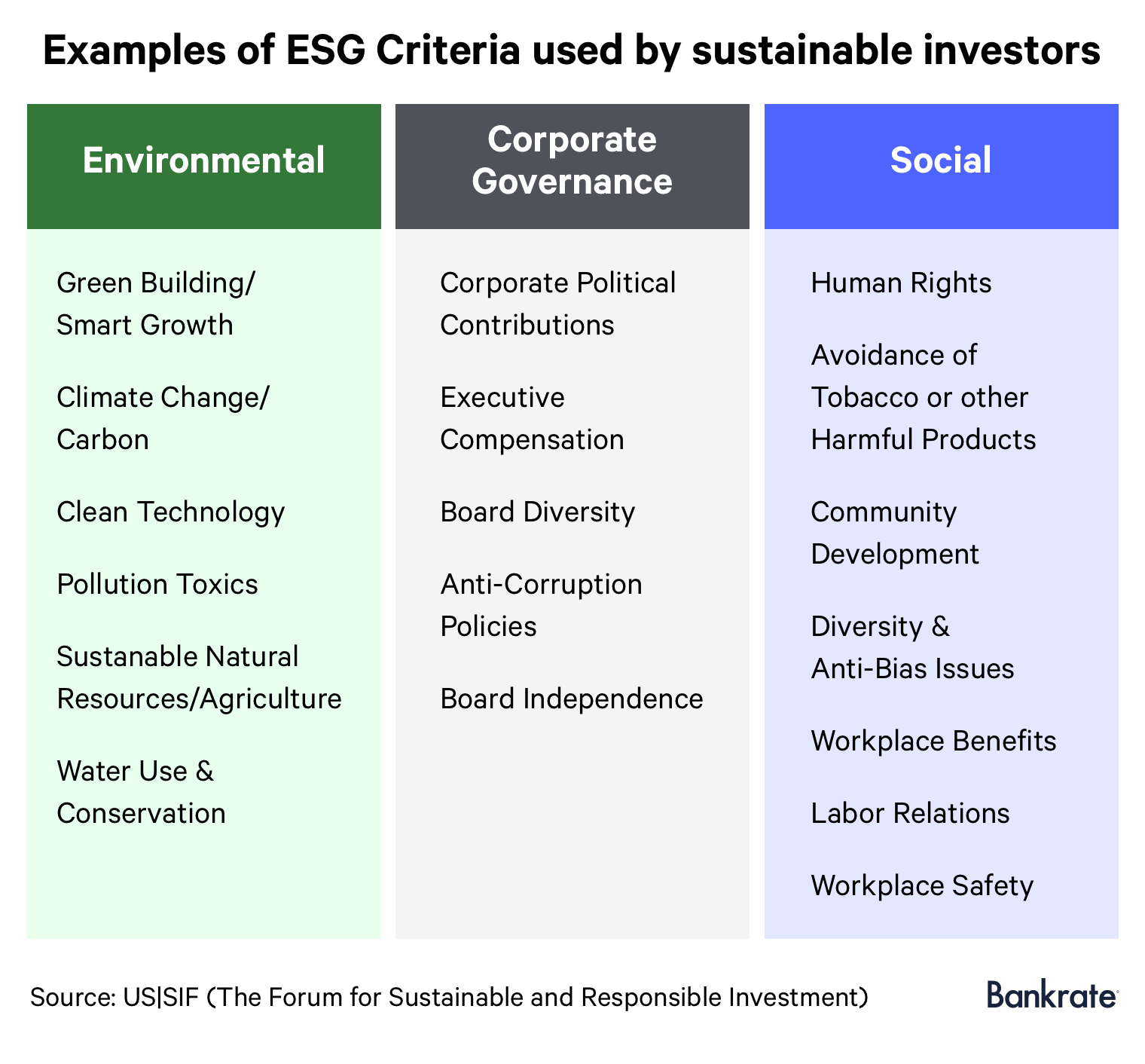
What is an ESG factor example : Key ESG Factors
These ESG factors can often be measured (e.g., what the employee turnover for a company is), but it can be difficult to assign them a monetary value (e.g., what the cost of employee turnover for a company is).
What is considered ESG
ESG stands for environmental, social and governance. These are called pillars in ESG frameworks and represent the 3 main topic areas that companies are expected to report in.
What are the 3 pillars of ESG : The three pillars of ESG are:
- Environmental – this has to do with an organisation's impact on the planet.
- Social – this has to do with the impact an organisation has on people, including staff and customers and the community.
- Governance – this has to do with how an organisation is governed. Is it governed transparently
This type of ethical investing strategy helps people align investment choices with personal values. ESG stands for environment, social and governance.
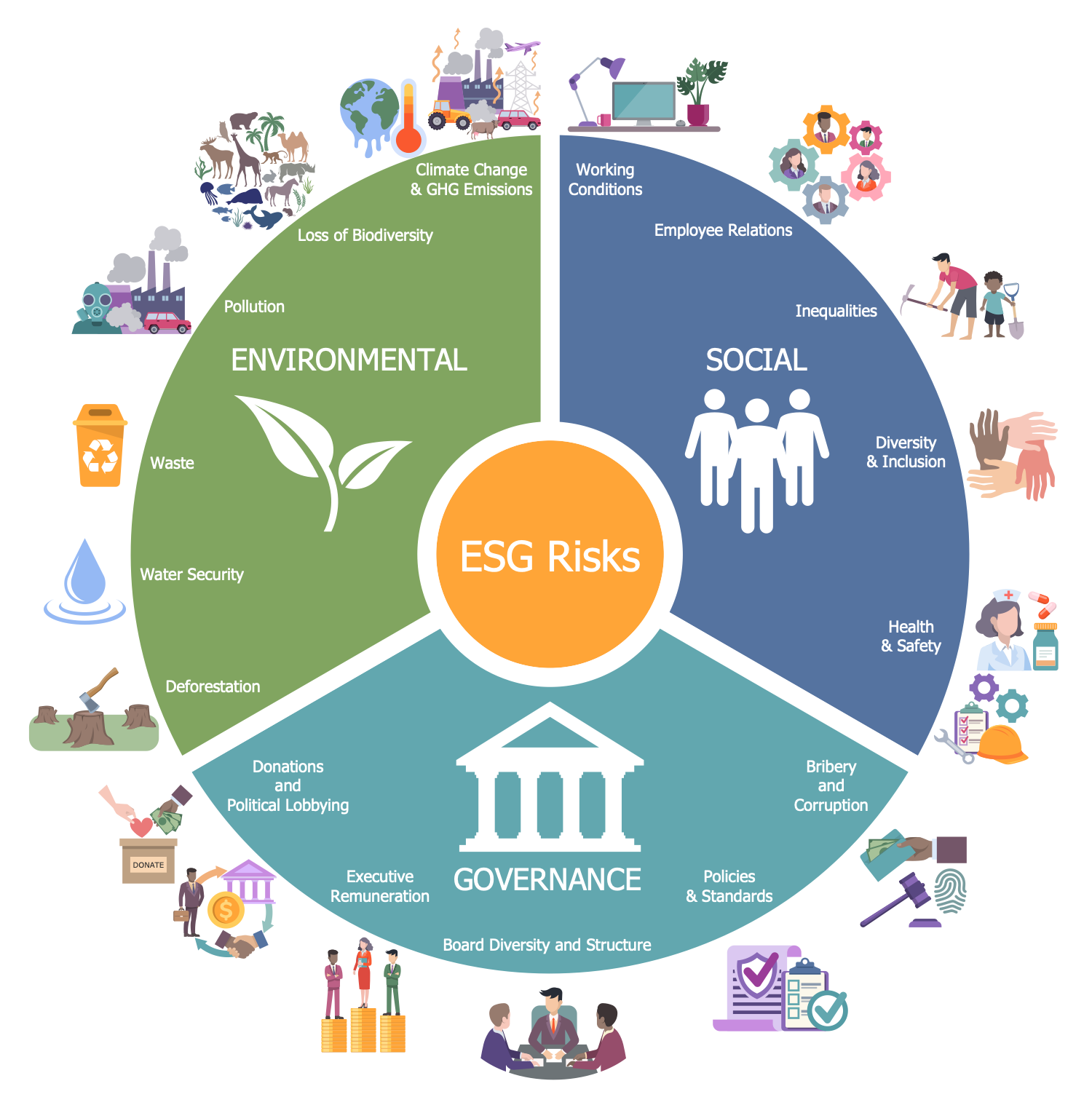
The following is an overview of the top globally employed ESG strategies.
- ESG Integration.
- Corporate Engagement and Shareholder Action.
- Norms-based Screening.
- Negative/Exclusionary Screening.
- Best-in-Class/Positive Screening.
- Sustainability-Themed/Thematic Investing.
What is the best explanation of ESG
What is ESG explained in simple terms ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a framework used to evaluate a company's sustainability and ethical impact.Critics portrayed ESG investing as primarily motivated by political concerns and a potential drag on returns. Additionally, some critics have raised concerns about the complexity and reliability of ESG metrics.In this context, the Big 4 accounting firms – Deloitte, PwC, Ernst & Young (EY), and KPMG – play a pivotal role in shaping corporate strategies, reporting practices, and, ultimately, the sustainability divide.

Environmental and societal issues, such as climate change, biodiversity loss, modern slavery, inequalities, food security and others are interconnected and lead to risks and opportunities for both, businesses, and society.
Why don’t people like ESG : There is no standard ESG benchmark. The people who do not support ESG are the ones who want to make money.” In a nutshell, “opponents to ESG argue that consideration of factors undermines corporate competitiveness and will lead to lower returns for shareholders,” says Maloney.
Is ESG the same as sustainability : Sustainability and ESG (environmental, social and governance) are initiatives that have become imperative in business with the threat of climate change and climate risk. The main difference between these two frameworks for business is ESG is a measured assessment of sustainability using benchmarks and metrics.
Why are esgs controversial
Critics say ESG investments allocate money based on political agendas, such as a drive against climate change, rather than on earning the best returns for savers.

In December 2022, Florida announced that it was taking $2 billion out of the management of BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager (and biggest lightning rod for ESG criticism). This was the largest such divestment thus far. These attacks have been coordinated.The Ps refer to People, Planet, and Profit, also often referred to as the triple bottom line. Sustainability has the role of protecting and maximising the benefit of the 3Ps. Green programs take care of people.
Why is ESG flawed : Like many economic factors, ESG factors exhibit diminishing returns, and trade-offs exist. Some ESG factors, such as employee satisfaction, have diminishing returns to scale but linear costs. Other ESG factors have hump shape relationships and ultimately negative returns.



